Pythonで、GUIアプリを作るには、Tkinterというライブラリを使う方法があります。
Tkinterでは、ウィジェットというGUI部品を、ウィンドウに配置することで、GUIアプリを作っていきます。
ウィジェットを配置する方法は、pack、grid、placeという3つの方法があります。
今回は、placeという方法を紹介します。
「place」の使い方
「place」の使い方は、以下のページで紹介しています。
サンプルコード
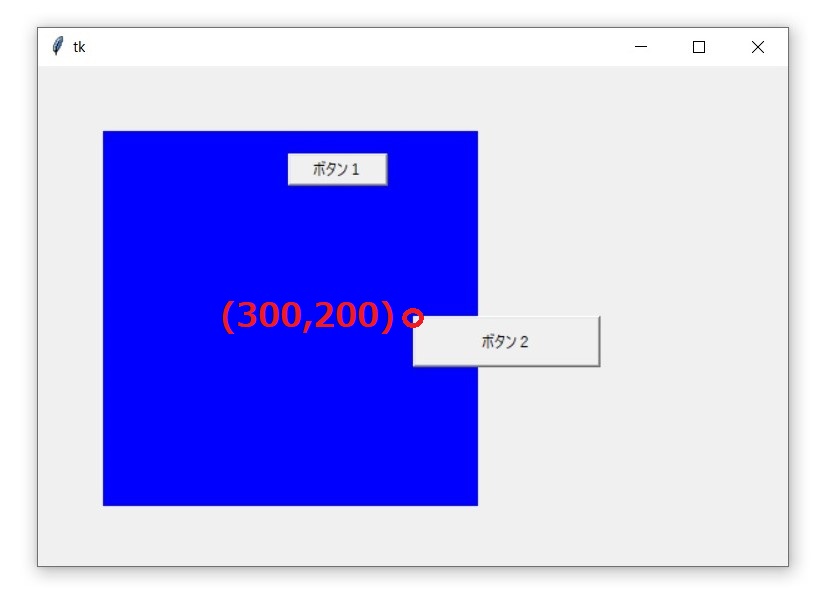
x、yの使い方
#!usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
# メインウィンドウ作成
app = Tk()
app.geometry("600x400")
# 青色のキャンバス作成
canvas1 = Canvas(
app,
width=300,
height=300,
bg="blue"
)
# 1つ目のボタン作成
button1 = Button(
app,
width=10,
height=1,
text="ボタン1"
)
# 2つ目のボタン作成
button2 = Button(
app,
width=20,
height=2,
text="ボタン2"
)
# ウィジェットの配置
canvas1.place(
x=50,
y=50
)
button1.place(
x=200,
y=70
)
button2.place(
x=300,
y=200
)
# メインループ
app.mainloop()
実行結果

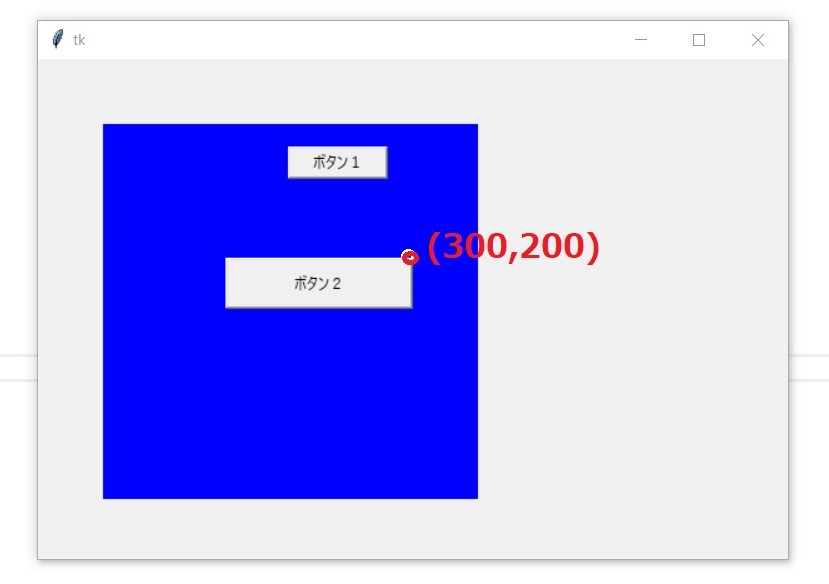
anchorの使い方
#!usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
# メインウィンドウ作成
app = Tk()
app.geometry("600x400")
# 青色のキャンバス作成
canvas1 = Canvas(
app,
width=300,
height=300,
bg="blue"
)
# 1つ目のボタン作成
button1 = Button(
app,
width=10,
height=1,
text="ボタン1"
)
# 2つ目のボタン作成
button2 = Button(
app,
width=20,
height=2,
text="ボタン2"
)
# ウィジェットの配置
canvas1.place(
x=50,
y=50
)
button1.place(
x=200,
y=70
)
button2.place(
x=300,
y=200,
anchor=NE
)
# メインループ
app.mainloop()
実行結果

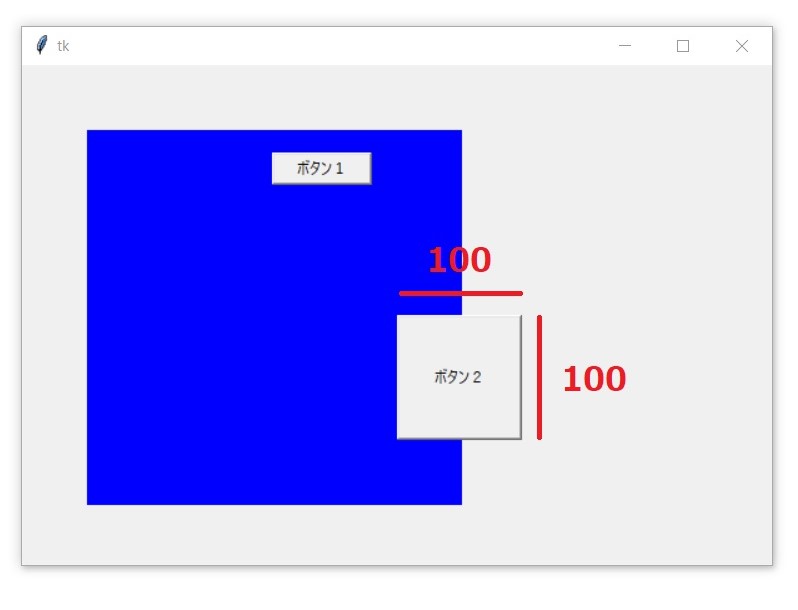
width、heightの使い方
#!usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
# メインウィンドウ作成
app = Tk()
app.geometry("600x400")
# 青色のキャンバス作成
canvas1 = Canvas(
app,
width=300,
height=300,
bg="blue"
)
# 1つ目のボタン作成
button1 = Button(
app,
width=10,
height=1,
text="ボタン1"
)
# 2つ目のボタン作成
button2 = Button(
app,
width=20,
height=2,
text="ボタン2"
)
# ウィジェットの配置
canvas1.place(
x=50,
y=50
)
button1.place(
x=200,
y=70
)
button2.place(
x=300,
y=200,
width=100,
height=100
)
# メインループ
app.mainloop()
実行結果

relx、relyの使い方
#!usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
# メインウィンドウ作成
app = Tk()
app.geometry("600x400")
# 青色のキャンバス作成
canvas1 = Canvas(
app,
width=300,
height=300,
bg="blue"
)
# 1つ目のボタン作成
button1 = Button(
app,
width=10,
height=1,
text="ボタン1"
)
# 2つ目のボタン作成
button2 = Button(
app,
width=20,
height=2,
text="ボタン2"
)
# ウィジェットの配置
canvas1.place(
x=50,
y=50
)
button1.place(
x=200,
y=70
)
button2.place(
relx=0.5,
rely=0.5
)
# メインループ
app.mainloop()
実行結果
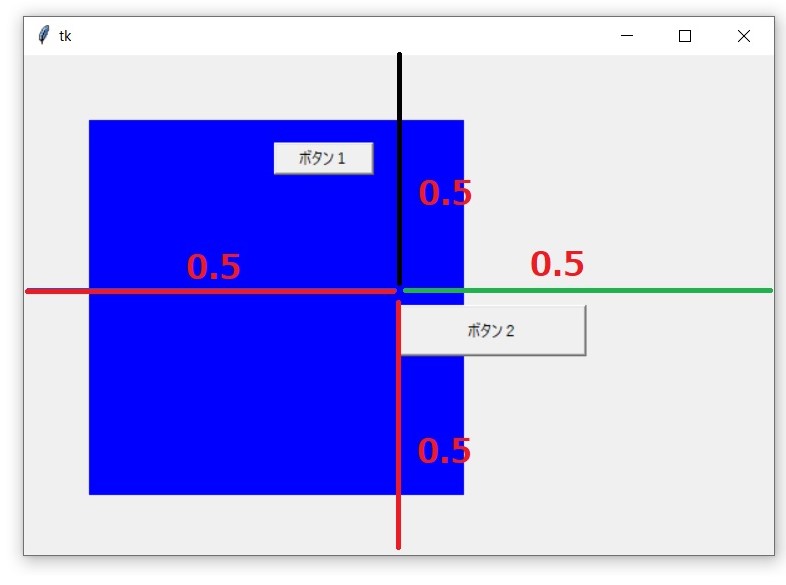

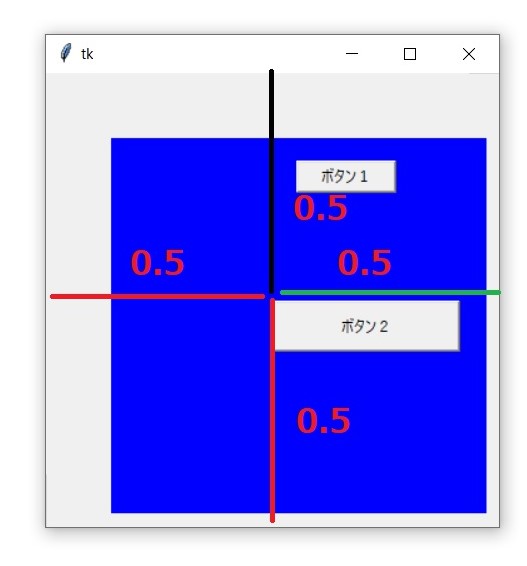

relwidth、relheightの使い方
#!usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
# メインウィンドウ作成
app = Tk()
app.geometry("600x400")
# 青色のキャンバス作成
canvas1 = Canvas(
app,
width=300,
height=300,
bg="blue"
)
# 1つ目のボタン作成
button1 = Button(
app,
width=10,
height=1,
text="ボタン1"
)
# 2つ目のボタン作成
button2 = Button(
app,
width=20,
height=2,
text="ボタン2"
)
# ウィジェットの配置
canvas1.place(
x=50,
y=50
)
button1.place(
x=200,
y=70
)
button2.place(
relwidth=0.3,
relheight=0.1,
relx=0.5,
rely=0.5
)
# メインループ
app.mainloop()
実行結果
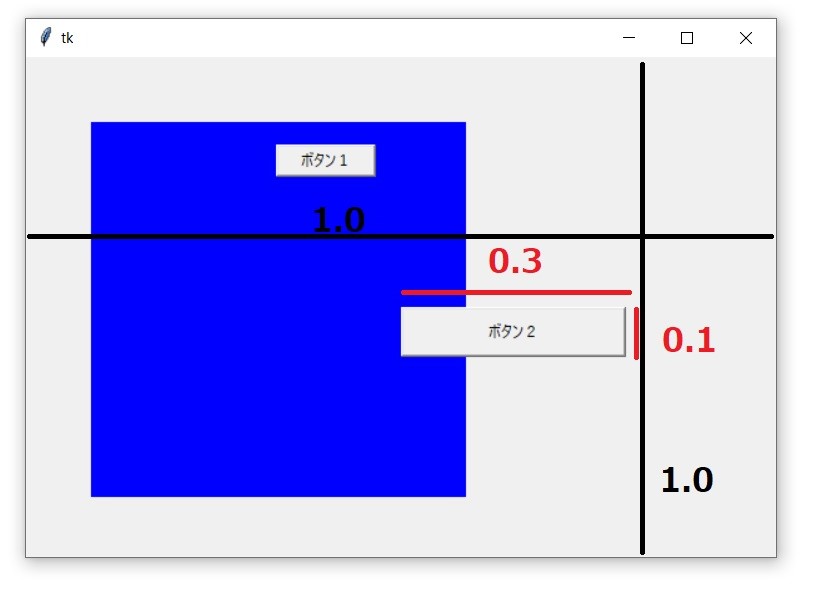

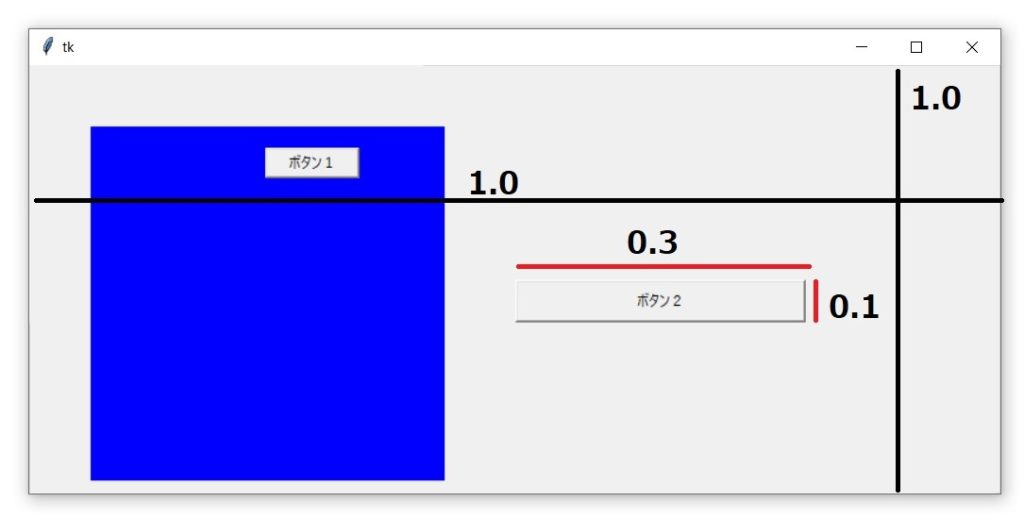

まとめ
Tkinterで、ウィジェットを配置する方法として、placeを紹介しました。
リンク







コメント